Dangerous goods are those substances or materials that can endanger health, safety, the environment and property. They can be solid, liquid or gaseous and are subject to strict regulations indicating requirements for storage, handling and transport.
The damage can be caused by the substance itself or by the reaction caused by contact with other substances.
Classification
Dangerous goods are classified according to the type of risk they represent. The United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) distinguishes nine classes or categories.
- Class 1. Explosive materials and objects.
- Class 2. Gases.
- Class 3. Flammable liquids.
- Class 4. Flammable solids.
- Class 5. Oxidizing substances and organic peroxides.
- Class 6. Toxic and infectious substances.
- Class 7. Radioactive materials.
- Class 8. Corrosive substances.
- Class 9. Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles.
Labels
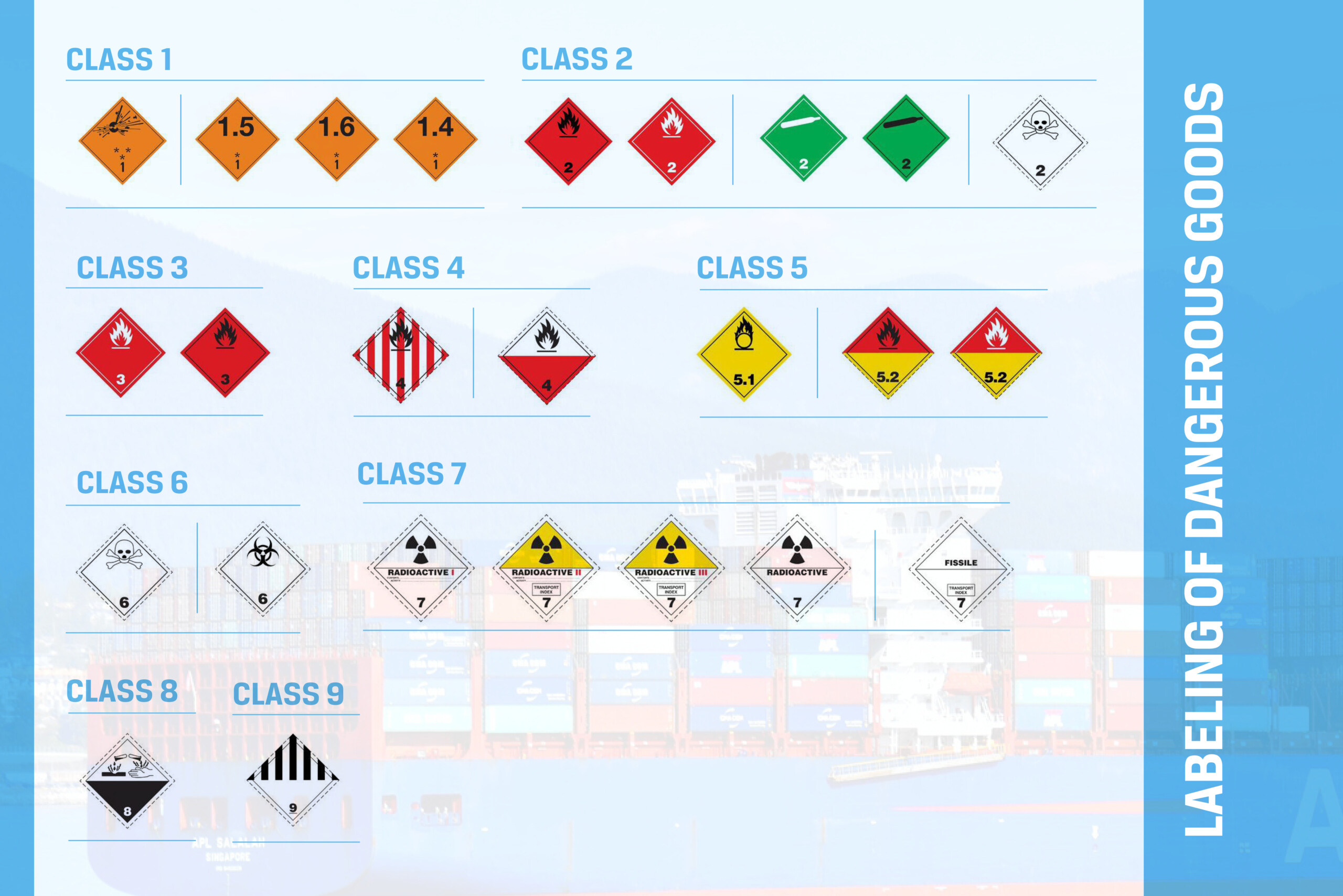
Each classification is identified with labels that express the risks of the goods when they are transported. The international ADR regulations include the following types.
Class 1
- Label with a black bomb explosion icon on an orange background and the number 1 at the bottom. Used for three subcategories of Class 1: substances with a mass explosion hazard; goods with a projection hazard; substances with a slight fire, blast or projection hazard.
- Orange label with the number 1 at the bottom and, in the top half the number of each of the subdivisions they represent (1.4; 1.5; 1.6): substances and articles having a low risk of explosion in the event of ignition; substances which are very insensitive to mass explosion; articles which are extremely insensitive to mass explosion
Class 2
- Label with a black or white flame on a red background with the number 2 at the bottom, identifies flammable gases.
- Label with a black cylinder or bench on green background with the number 2 at the bottom, identifies non-flammable, non-toxic gases.
- Label with a black skull on white background with the number 2 at the bottom, is used for toxic gases.
Class 3
- Label with a black or white flame on a red background with the number 3 at the bottom.
Clase 4
- Label with a black flame on a background with vertical red and white stripes, with the number 4 at the bottom, is used for flammable solids.
- Label with a black flame on a background with the upper half white and the lower half red, with the number 4 at the bottom, identifies substances that can undergo spontaneous combustion.
Class 5
- Label with a black icon symbolizing a flame on a circle, on a yellow background and the number 5.1 at the bottom, indicates oxidizing substances.
- Label with a black or white flame on a background with the upper half red and the lower half yellow and the number 5.2 in the lower part, identifies organic peroxides.
Class 6
- Label with a black skull on a white background with the number 6 at the bottom, is used for toxic substances.
- Label with the black symbol of three crescents superimposed on a circle, with a white background, and the number 6 at the bottom, is used for infectious substances.
Class 7
- Label with a black clover on a white background at the bottom is indicated the category I and data regarding content, radioactivity, etc.
- Label with a black clover on a yellow background at the bottom is indicated the category (II or III, with a higher level of hazard) and data regarding contents, level of radioactivity, etc.
- White label “FISSILE” in black text and in the lower part “CRITICALLY SAFETY INDEX” next to the number 7, identifies fissile material.
Class 8
- Label with two black test tubes. One pours a corrosive substance onto a surface and the other onto a hand. The background of the top is white, and the bottom is black with the word “CORROSIVE” next to the number 8.
Class 9
- Label with vertical black and white stripes on the top half and the number 9 on the bottom.